|
|
7+7 Risk Matrix cont...Send comments on this topic |
FREE QHSE Software Click <HERE> to Learn More |
||
QHSE Support >(Site Map) Health & Safety Guidance > Risk Assessments >
Health and Safety Risk Assessments - Sample 7+7 Risk Assessment Matrix page 2 of 2
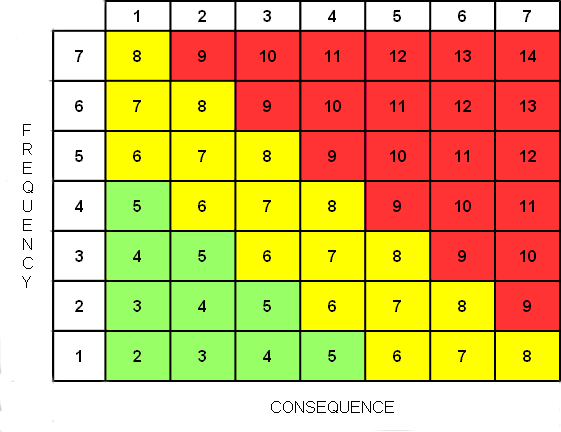
Risk Rating = Frequency (Likelihood) ranking + Consequence ranking
It is very important to note however, that adding the frequency and consequence rankings only works if the changes in both the frequency and consequence estimates (as represented by the changes in their corresponding ranking numbers) are separated by the same factor.
This solution works for any factor difference (two, five, ten, one hundred, etc.) providing both the frequency and consequence ranking estimates are separated by the same factor.
Events with the potential for significantly different outcomes
When assigning frequency and consequence rankings to hazardous events the rankings are based normally on the average frequency of occurrence and the average consequences for the event. For some hazardous events, however, different outcomes can lead to significantly different consequences. For example, a train derailment would typically only lead to minor injuries, due perhaps to passengers falling over inside the train, whereas in extreme cases, derailments can lead to multiple fatalities. It is recommended that in such cases, to get a better understanding of the risk profile, particularly in relation to potential multi-fatality outcomes, two separate rankings should be considered for the hazardous event as follows:
a) the first ranking should relate to the frequency and consequences of the typical (most frequent outcome),
and
b) the second risk ranking should relate to the frequency and consequences of the realistic worst case outcome, if appropriate.
Help file v2.276.407 : QHSE Support - Website On Safe Lines
onsafelines.com QHSE Software 2025 : Webmaster: Brian G. Welch MSc(QHSE), NVQ4(OH&S), CMIOSH