|
|
ISO 9001-2015 6.2 ObjectivesSend comments on this topic |
FREE QHSE Software Click <HERE> to Learn More |
||
QHSE Support >(Site Map) Quality Guidance > ISO 9001-2015 Clauses > ISO 9001-2015 clause 6 >
ISO 9001:2015 Clause 6.2 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them
|
PLAN |
DO |
CHECK |
ACT |
Quality objectives must be understandable and accepted. They can be set with a timebase which is short, medium or long-term and have an operational, strategic or tactical framework, as well as being financial, quality, safety, environmental, customer based etc., or combinations thereof.
The plan, do, check, act cycle is very much the ideology for which the standard is driving organizations to embrace.
The PDCA cycle can be briefly described as follows:
- Plan: establish the objectives of the system and its processes, and the resources
needed to deliver results in accordance with customers’ requirements and the organization’s policies, and identify and address risks and opportunities;
- Do: implement what was planned;
- Check: monitor and (where applicable) measure processes and the resulting products and services against policies, objectives, requirements and planned activities, and report the results;
- Act: take actions to improve performance, as necessary.
It can be seen that 'objectives' play a key role in meeting the requirements of the plan, do, check, act cycle and are therefore essential to meeting the ethos of the ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management standard.
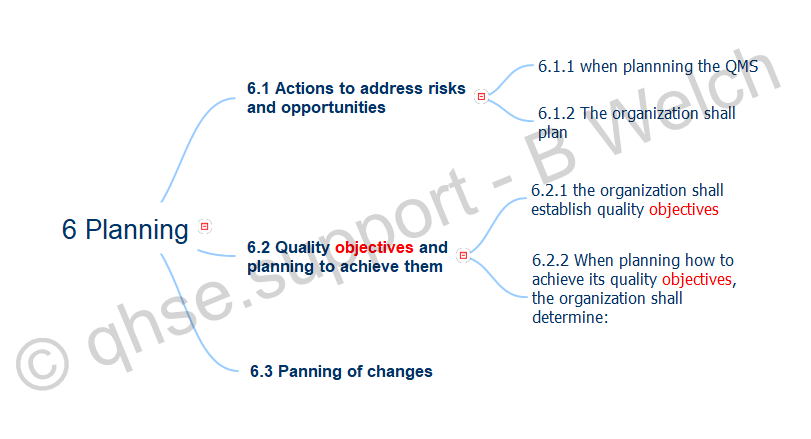
Clause 6.2 Breakdown
6.2 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them
6.2.1 (establish quality objectives)
6.2.2 (achieve quality objectives)
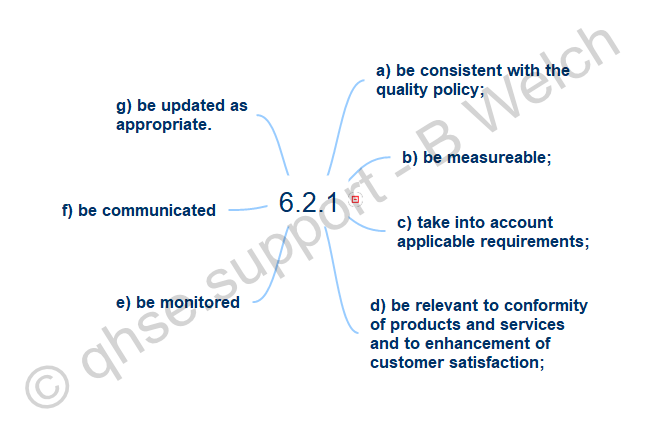
Quality objectives shall be consistent with the quality policy can be seen in clause 3.5.9(1) and 3.7.1(4) of ISO 9000:2015.
3.5.9 quality policy - policy related to quality
Note 1 to entry: Generally the quality policy is consistent with the overall policy of the organization, can be aligned with the organization’s vision and mission and provides a framework for the setting of quality objectives.
3.7.1 objective - result to be achieved
Note 4 to entry: In the context of quality management systems quality objectives are set by the organization, consistent with the quality policy, to achieve specific results.
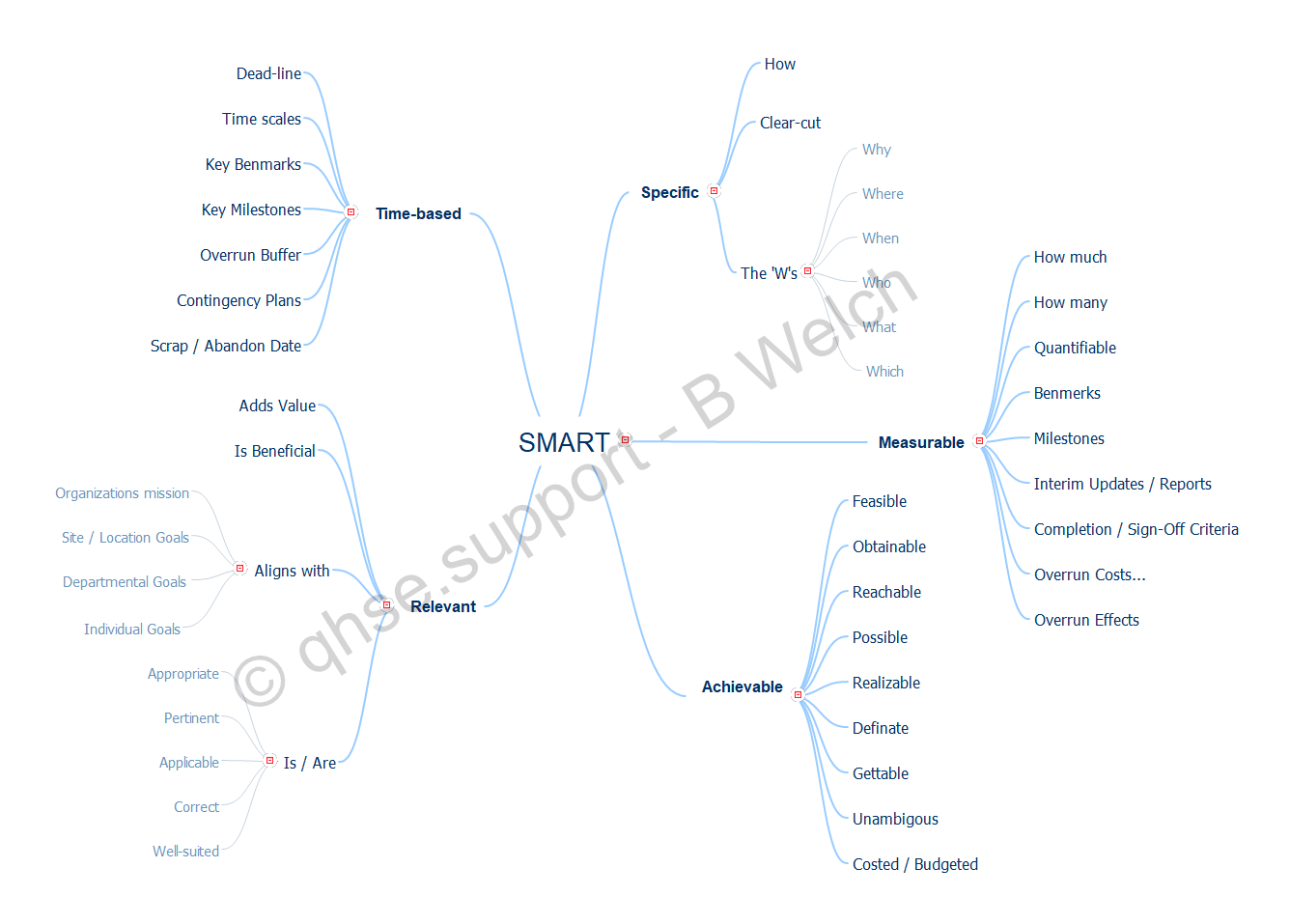
Quality objectives can be seen as targets, goals to be achieved and as such are measurable. The ability to measure objectives allows an organization to be able to report on the effectiveness of their QMS system. That said, creating objectives should be done using techniques such as SMART, i.e. Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-based, and beyond this well known acronym and equally as important they should be 'understandable'. It should also be pointed out that objectives that are too easily achieved risk the integrity of the overall organization QMS plausibility.
There are many different terms used to define the acronym SMART as well as many and varied interpretations of each specific letter, below is a mind map showing one example.
 Whilst quality objectives are related to "the context and strategic direction of the organization", many organizations will also set objectives as Key Performance Indicators (KPI's) that cascade downwards company-wide to individual level, for example:
Whilst quality objectives are related to "the context and strategic direction of the organization", many organizations will also set objectives as Key Performance Indicators (KPI's) that cascade downwards company-wide to individual level, for example:
Level 1 - Organization
Level 2 - Location / Site
Level 3 - Department /Team
Level 4 - Individual
KPI's tend to be process driven, whereas quality objectives are mainly aimed at an organizational level. It could be seen that KPI's are the measures that indicates if your on route to achieving the organizations quality objectives or not.
The balance here is that for ISO 9000:2015 3.7.8 performance is defined as "measurable result" whereas ISO 9000:2015 3.7.1 objective means "result to be achieved".
Useful integrated management system cross references
ISO 14001
•ISO 14001-2015 6.2 Objectives
ISO 45001
•ISO 45001-2018 6.2 Objectives
Help file v2.276.407 : QHSE Support - Website On Safe Lines
onsafelines.com QHSE Software 2025 : Webmaster: Brian G. Welch MSc(QHSE), NVQ4(OH&S), CMIOSH