|
|
5x5 Risk Matrix - part 1Send comments on this topic |
FREE QHSE Software Click <HERE> to Learn More |
||
QHSE Support >(Site Map) Health & Safety Guidance > Risk Assessments >
Health and Safety Risk Assessments - Sample 5x5 Risk Assessment Matrix page 1 of 5
5x5 Risk Assessment Sections
•5x5 Risk Matrix - part 1
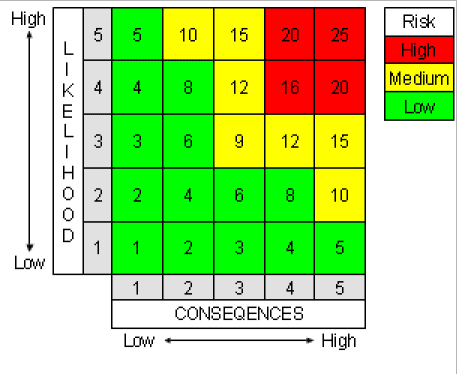
The matrix works by selecting the appropriate consequences from across the bottom, and then cross referencing against the row containing the likelihood, to read off the estimated risk rating.
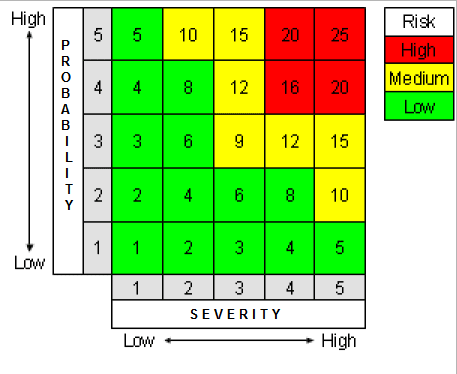
Two examples of risk assessment matrix 5x5 using different axis labels.
Examples of a Likelihood verses Consequences 5x5 Risk Assessment Matrix and a Probability verses Severity 5x5 Risk Assessment Matrix
|
Probability x Severity version supplied by John Cronjaeger, Airworthiness Technical Assistant, London Executive Aviation Ltd |
See additional 5x5 risk matrix's
Likelihood (Probability)
5. Almost Certain
4. Probable
3. Possible
2. Possible (under unfortunate circumstances)
1. Rare
Consequences (Impact)
5. Fatality
4. Major Injury, resulting in disability
3. Injury Requires, Doctor's or Hospital attendance
2. Minor Injury, 1st Aid required
1. Minor Injury, 1st Aid not required
Risk matrix 5x5 breakdown (Also see alternatives impact groupings)
Risk Rating is calculated by multiplying the likelihood against the consequences, e.g. taking a likelihood of 4, which is classified as Probable, and multiplying this against a consequence of 2, which is classified as a Minor Injury 1st aid required, would give you and overall risk rating of 8, which would be risk rated as a low risk.
Low risk equals 1 to 8.
Low Risks are largely acceptable, subject to reviews periodically, or after significant change etc...
Medium risk equals 9 to 15.
Medium Risks should only be tolerated for the short-term and then only whilst further control measures to mitigate the risk are being planned and introduced, within a defined time period. Note: Medium risks can be an organisations greatest risk, it's Achilles heel, this due to the fact that they can be tolerated in the short-term.
High risk equals 16 to 25.
High Risks activities should cease immediately until further control measures to mitigate the risk are introduced.
Faults in the 5x5 matrix.
The 5x5 matrix below shows more readily that risks may not always be broadly classified in to three categories. If we take the two extremes of the medium risk range in the matrix above, we can see that both 9 and 15 sit in the yellow range. However, in the matrix below 9 sits just above and moving out of the green, whereas 15 sits just below and moving into the red range. It can become all to easy for potential risks to be classified in the medium range and management to undertake a tick the box exercise...
Help file v2.276.407 : QHSE Support - Website On Safe Lines
onsafelines.com QHSE Software 2025 : Webmaster: Brian G. Welch MSc(QHSE), NVQ4(OH&S), CMIOSH